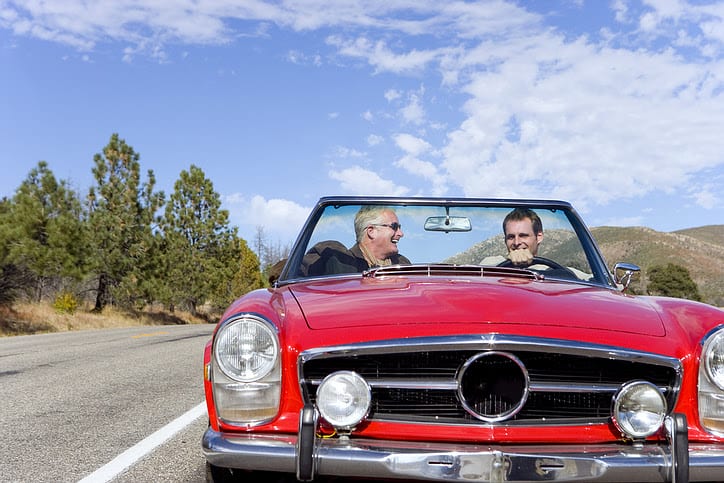
New Mileage Rates for 2021
February 15, 2021
New Child Tax Credit Benefits for 2021
June 29, 2021|
The Treasury Department and Internal Revenue Service announced today that the federal income tax filing due date for individuals for the 2020 tax year will be automatically extended from April 15, 2021, to May 17, 2021. The IRS will be providing formal guidance in the coming days.
Individual taxpayers can now postpone federal income tax payments for the 2020 tax year due on April 15, 2021, to May 17, 2021, without penalties and interest, no matter what amount is owed. The postponement applies to individual taxpayers, including people who pay self-employment tax. Penalties, interest, and additions to tax will start to accrue on any remaining unpaid balances as of May 17, 2021. Individual taxpayers will automatically avoid interest and penalties on the taxes paid by May 17.
Taxpayers won’t need to file any forms or call the IRS to qualify for the automatic federal tax filing and payment relief. Individuals who need extra time to file beyond the May 17 deadline can ask for a filing extension until Oct. 15 by filing Form 4868 through their tax preparer or DIY tax prep software, or by using the Free File link on IRS.gov. Filing Form 4868 gives taxpayers until Oct. 15 to file their 2020 tax return but doesn’t provide an extension of time to pay any taxes that due. The IRS said taxpayers should pay their federal income tax due by May 17, 2021, so as to avoid extra interest and penalties.
Despite the extension, the IRS is urging taxpayers who are due a refund to file as quickly as possible. Most tax refunds associated with electronically filed returns are sent within 21 days.
The relief doesn’t apply to estimated tax payments that come due on April 15. Those payments are still going to be due on April 15. The taxes have to be paid as taxpayers earn or receive income during the year, either via withholding or estimated tax payments. Typically, estimated tax payments go out quarterly to the IRS from people whose income isn’t subject to income tax withholding, including self-employment income, interest, dividends, alimony or rental income. Most taxpayers automatically have their taxes withheld from their paychecks and sent to the IRS by their employer.
|